News Center
- Company News
Company News
- Industry News
Industry News
Xinmin Weekly: AI Empowers Healthcare, China's Practice Accelerates AI+Medical Exploration at Huashan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University
In early 2025, DeepSeek sparked an "AI whirlwind" in China, showcasing to the world China's true prowess in AI application innovation. In the medical field, the systematic transformation brought about by AI enhancement across the entire medical process is not only a focal point of global industry attention, but also a project that concerns national development and people's well-being.
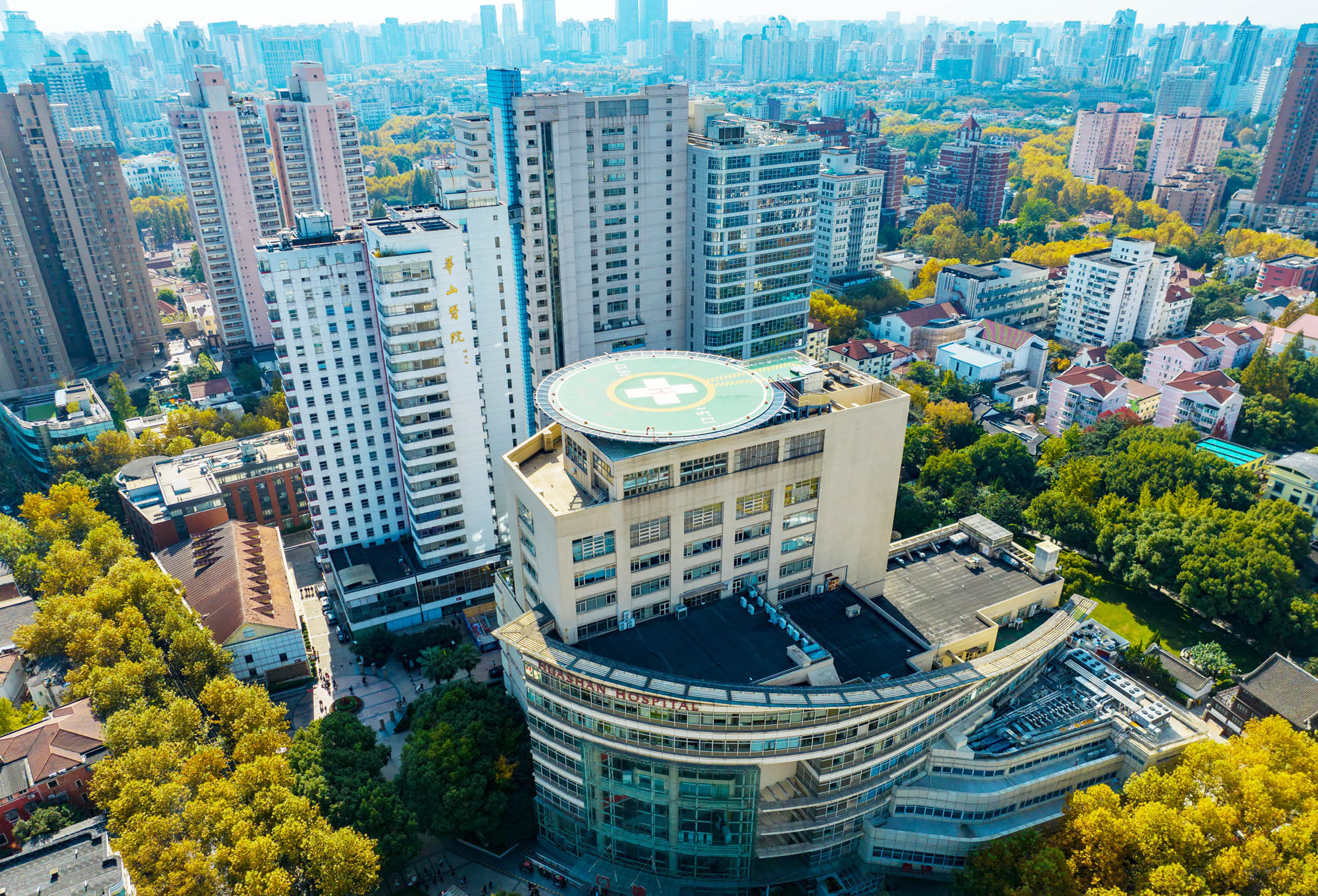

Huashan Hospital Outdoor Scene
Established in 1907, Huashan Hospital affiliated with Fudan University has been a highland of medical innovation for over a hundred years. The hospital undertakes the construction of three national level medical centers, namely the National Center for Neurological Diseases, the National Center for Infectious Diseases, and the National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Diseases. Its comprehensive strength in disciplinary groups, ability to diagnose and treat difficult diseases, medical radiation capability, and technological innovation capability have attracted much attention.
In recent years, the hospital has been committed to the forefront exploration of "AI+healthcare" as a "national team". With the support of the Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Health Commission, the Shanghai Municipal Government and relevant departments, and Fudan University, relying on the three national medical centers and 20 national key clinical specialties and 10 national key disciplines throughout the hospital, we first focus on innovative exploration in key areas such as neurology, infection, elderly care, and dermatology, and promote high-quality "AI+healthcare" to truly land in clinical practice.
Zheng Ning, Secretary of the Party Committee of Huashan Hospital, stated that as a national level large public hospital, the hospital adheres to the principle of using data and artificial intelligence technology to serve the real problems and scenario needs of medicine. Through bold innovative practices, it explores the development of the hospital and disciplines, and empowers the solution to key issues in the medical field.
Mao Ying, the director of Huashan Hospital, emphasized in an interview that imaging, molecular biology, information and other technologies have provided important engines for the development of modern medicine, but at the same time, individual doctors also have natural limitations in processing massive amounts of data. As a powerful auxiliary tool, AI can greatly improve the efficiency of medical clinical and scientific research, empowering every doctor to have the "strongest brain" and obtain important decision support. The ultimate goal of Huashan Hospital's AI innovation practice is to bring more effective treatment, warmer medical experience, and more clinically valuable innovative drugs and technologies to patients.
In 2022, the "14th Five Year Plan" for National Health Informatization clearly emphasizes the promotion of AI applications in key areas such as disease screening, image recognition, and drug research and development. The 2025 State Council Government Work Report further proposes to continue promoting the "Artificial Intelligence+" initiative. As a strategic technology leading the new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation, artificial intelligence's deep integration with biomedicine is also a key industrial direction for Shanghai's layout.
With the acceleration of the national strategic deployment of "AI+healthcare", Huashan Hospital's forward-looking series of explorations not only pave the way for future medical forms, but also explore valuable practical experience in helping Shanghai build a globally influential technology innovation center, serving major national strategic missions, and promoting the implementation of the "Healthy China 2030" goal.
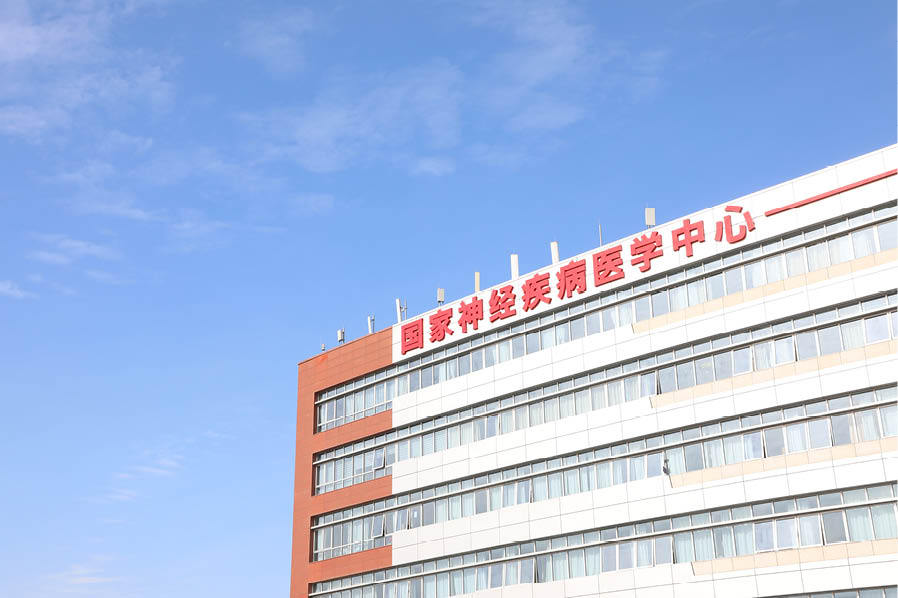

Through deep interdisciplinary integration, the National Center for Neurological Diseases has built a clinical and basic platform with original driving capabilities, systematically tackling difficult diseases for diagnosis and treatment
AI assisted, "precision diagnosis and treatment" enters a new era
Accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment are the "ideal realm" pursued by medicine. Nowadays, with the help of AI, "precision medicine" is entering a new stage.
The Neurosurgery Department of Huashan Hospital is an important birthplace of neurosurgery in China and also the location of the National Center for Neurological Diseases. It has been evaluated by the most authoritative international neurosurgery journal, Neurosurgery, as one of the best neurosurgery centers in the world. The department, together with more than ten related disciplines such as neurology, radiology and rehabilitation, and industry university research institutions such as the State Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology, the Institute of Brain Science, and the Institute of Brain Science Transformation, has built a clinical and basic platform with the ability to drive innovation, and systematically tackle difficult diseases.
Gliomas are highly challenging malignant tumors in the field of neurosurgery, accounting for 40% to 50% of brain tumors and 70% of primary malignant brain tumors. They are known as "brain killers" and their invasive characteristics and diffuse growth patterns in language, motor, and cognitive functional areas have long constrained the achievement of precise surgical resection. In the early stages, the diagnosis of glioblastoma mainly relied on traditional histopathology, but due to the heterogeneity of tumors, it is often "same disease, different fate", and there are significant differences in prognosis judgment and prediction of therapeutic effects.
Accurate diagnosis is a core component of the comprehensive diagnosis and treatment system for glioma.
Professor Mao Ying, President and Executive Deputy Director of Neurosurgery at Huashan Hospital, led a team with the strong support of Academician Zhou Liangfu. Over a decade ago, they began exploring the "precision" diagnosis and treatment of gliomas through digital transformation. After 8 years of deciphering the metabolic code of gliomas, they proposed the "Huashan Plan" for glioma molecular typing, contributing the "Shanghai Wisdom" to the global transition from histological diagnosis to molecular diagnosis of gliomas.
Afterwards, the team continued to use digital technology to obtain glioma molecular information from medical images such as MRI and ultrasound, and developed a molecular visualization surgical navigation system, making "invisible" molecular diagnostic data truly "visible", achieving molecular level resection of brain gliomas, significantly reducing residual tumor cells, while protecting brain function and improving postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy efficacy. Taking glioblastoma, which has the highest degree of malignancy among all nerve tumors, as an example, the median survival time of patients has increased from 13.2 months to 17.6 months, significantly better than the internationally reported average survival time of 14.6 months.
With the development of AI technology, a large amount of information can be efficiently extracted and transformed into support for personalized clinical decision-making. The Huashan Hospital team has built a multimodal neural tumor intelligent decision-making platform based on a rapid molecular diagnostic system, and proposed a series of innovative concepts such as "quantitative pathology". By integrating multiple immunohistochemistry techniques and machine learning algorithms, it provides a highly interpretable decision-making tool for clinical practice. At the same time, the team collaborated with ShanghaiTech University to develop a "personalized patient tumor organoid" model, which can construct a highly simulated tumor microenvironment and heterogeneity model in just two to three weeks, enabling more accurate prediction of chemotherapy drug response and resistance mechanisms, achieving a major breakthrough in precision medicine for brain tumors.
Empowered by AI, today's neurosurgery is completely different from traditional surgery. During surgery, doctors can use mass spectrometry technology to achieve rapid molecular diagnosis within 1.5 minutes, and combine Raman spectroscopy technology to obtain richer metabolomics information; Targeted molecular localization and visualization of pathological features can be achieved through precise fluorescence probe technology. With the assistance of AI, this rich information can be quickly integrated to assist doctors in making real-time surgical decisions and accurately drawing surgical boundaries. Doctors can provide clearer answers to key questions such as whether the lesion should be removed, how large the removal area needs to be, and what impact it will have on patients in the future.
The molecular visualization surgical navigation system makes the "invisible" pathological diagnostic data truly "visible", achieving molecular level resection for nerve tumors. The picture shows Professor Mao Ying's surgery
At the same time, the hospital has established multidisciplinary integrated wards centered on diseases, and through full process management, many patients with neurological tumors, including pituitary tumors, can achieve lifelong and high-quality survival.
In the field of cerebrovascular disease, cerebral aneurysms are known as "intracranial bombs", with high rates of death and disability caused by rupture. In this high difficulty and complex surgical decision-making field, relying on traditional experience for operation has significant limitations, high difficulty, and a long learning cycle for doctors. The intracranial aneurysm surgical planning software developed by Professor Gu Yuxiang's team in the neurosurgery department of Huashan Hospital uses AI analysis to reconstruct the three-dimensional morphological structure of aneurysms, automatically measure relevant parameters, provide suitable delivery paths and shaping needle shapes for each aneurysm, assist clinical doctors in making decisions, and has been approved for the National Medical Products Administration's innovative medical device Class III registration certificate, which has important clinical application value.
In September 2024, the China National Medical Products Administration issued a Class III medical device registration certificate, which is also the first Class III medical device registration certificate for intracranial aneurysm magnetic resonance AI in China, to the Huashan Hospital team. The "Intracranial Aneurysm Magnetic Resonance Imaging Assisted Detection Software" developed by Professor Geng Daoying's team from the Radiology Department of Huashan Hospital and the Engineering and Applied Technology Research Institute of Fudan University, relying on the National Center for Neurological Diseases, can assist doctors in detecting intracranial aneurysms of 3mm or more, quantitatively analyzing the lesion area, and providing relevant suggestions.
In addition, Professor Guan Ming, the director of the Department of Laboratory Medicine, has led the launch of an AI diagnostic system for cerebrospinal fluid cytology to assist in cerebrospinal fluid cytology examination. It has achieved precise diagnosis in 10 types of tumors, and the detection accuracy of the immunochemical staining detection model has reached over 95%.
Under the forward-looking layout, a series of research achievements have continuously emerged in the center in the past two years, published in top international journals such as The New England Journal of Medicine, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Cancer Cell, and Advanced Science. This not only breaks through the technological limits of existing neurological disease diagnosis and treatment, but also provides a "Chinese solution" for the development of precision medicine worldwide.

The opening cover of Cell magazine features the interdisciplinary research results of Chinese medical scientists. Through in-depth analysis of proteomic big data, a comprehensive proteomic map has been created, successfully uncovering highly promising biomarkers and therapeutic targets for disease prediction and diagnosis
In the field of elderly health, which is highly concerned by society, in July 2016, the only national clinical research center for geriatric diseases in East China settled in Huashan Hospital. The center actively participates in the strategic formulation of the national medium and long-term scientific and technological development plan in the field of population aging, undertakes national key research and development plans such as "Active Health and Aging Technology Response", and carries out systematic research and development around the bottleneck issues of healthy aging. In recent years, through system development, the center has established intelligent signal decoding solutions such as precise recognition of motion intentions and multimodal data analysis, and carried out the research and development of practical rehabilitation auxiliary intelligent devices such as flexible exoskeletons, high-performance prosthetics, and rehabilitation robots. The team relies on this theory to develop flexible exoskeleton intelligent assistive devices with enterprises. In 2024, 2 new invention patents were granted, and the product developed in cooperation with innovative enterprises has obtained a medical device registration certificate. The hand exoskeleton trainer (assistive device version) developed in cooperation has entered the "Shanghai Disabled Assistive Device Guidance Catalog".
From clinical diagnosis and treatment decision optimization to active rehabilitation, Huashan Hospital is transforming its full chain ecosystem empowered by AI technology from "single point breakthrough" to "system improvement", truly empowering the system to solve clinical "big problems", playing a leading role as a national medical center, and setting a benchmark for more disciplines to carry out "AI empowered precision diagnosis and treatment".
AI enhancement accelerates the development of new drugs and technologies
National level medical centers not only serve clinical practice, but also serve as a source of innovation for new technologies, drugs, and devices. With the help of "AI+healthcare", in recent years, Huashan Hospital has continuously promoted the landing of high-quality innovative technologies and provided an important platform for new drug research and development.
With the arrival of the era of deep aging, neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) have become major public health challenges. In the past, due to the scarcity of early biomarkers and the lack of disease modifying therapies, patients with neurodegenerative diseases often missed the golden intervention window when diagnosed. In this context, the team led by Professor Yu Jintai from the Department of Neurology at the National Center for Neurological Diseases and Huashan Hospital, together with research institutes such as the Institute of Brain Intelligence at Fudan University, have innovatively integrated neuroscience, multi omics technology, and artificial intelligence through the "Fudan University AI for Science (AI4S)" platform, achieving significant breakthroughs.
In the field of early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, the team used large-scale proteomic data and artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze and model 1463 types of plasma proteomic data, and discovered important plasma biomarkers for predicting future dementia risk, which can predict the risk of dementia 15 years in advance with an accuracy rate of over 90%. The related research results were published in Nature Aging, and the main journal of Nature evaluated this study as "a step towards a blood detection method that can detect Alzheimer's disease and other types of dementia in the early asymptomatic stage". On this basis, the team analyzed the largest cerebrospinal fluid proteome queue to date (covering 6361 proteins) through AI and discovered a novel biomarker - YWHAG, which has important value for the diagnosis and prediction of Alzheimer's disease. Through protein combination detection, the diagnostic accuracy can reach 98.7%, creating a critical time window for ultra early intervention.
Based on this research experience, in January of this year, the teams of Yu Jintai and Mao Ying collaborated with the teams of Cheng Wei and Feng Jianfeng from the Institute of Brain Intelligence Science and Technology to create the most comprehensive "human health and disease plasma proteome map" to date. By incorporating 1706 human diseases and phenotypes, a comprehensive proteome map was drawn, and with the help of machine learning models, highly potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for disease prediction and diagnosis were successfully discovered. The research results were featured on the cover of the 2025 issue of the journal Cell and were evaluated as "the first time that hundreds of disease risks can be predicted through a single peripheral blood test". This not only provides a key for human disease prediction, but also opens up new possibilities for life science research. New research paradigm.
Parkinson's disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer's disease. The global number of Parkinson's disease patients is expected to increase from around 7 million in 2015 to 13 million in 2040, with China accounting for approximately half of the global Parkinson's disease patient population.
Traditional medicine and surgical treatment only target the symptoms of Parkinson's disease and cannot delay disease progression. After 5 years of research, Yu Jintai's team has identified the "trigger" for the transmission of pathological alpha synuclein between neurons and discovered candidate new drugs that inhibit its transmission process. Subsequently, the research team utilized AI protein structure prediction and virtual screening techniques to successfully identify a small molecule from over 7000 small molecule compounds that can effectively inhibit the binding of FAM171A2 protein to pathological alpha synuclein and suppress the uptake of the pathogenic protein fibers by dopaminergic neurons. Research has found that targeting the novel target FAM171A2 can block the spread of pathological alpha synuclein and delay the progression of Parkinson's disease in the preclinical, prodromal, and clinical stages of the disease.
This research result, published in the top journal Science, will not only bring good news to millions of Parkinson's disease patients, but also mark a milestone breakthrough in China's biopharmaceutical field on the path of "original target discovery mechanism analysis product development" in the entire chain of independent innovation for Parkinson's disease.
In the field of medical prevention integration, Huashan Hospital is a national infectious disease medical center with infectious diseases and antibiotic research institutes as its core. It connects with key areas of health in China to build a strong public health system, and continues to explore the diagnosis and treatment of newly emerging infectious diseases, difficult to treat classic infectious diseases, and bacterial infections, promoting the transformation of disease prevention and control from "casting a wide net" to "precise targeting".
During the 2023 National People's Congress and Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, Professor Zhang Wenhong, Director of the Center and Director of the Department of Infectious Diseases at Huashan Hospital, systematically introduced the Center's AI exploration. By accelerating the analysis of multidimensional data such as epidemiology, environment, and genome, it can achieve ultra early warning of new infectious diseases and provide key support for pathogen identification, vaccine and new drug development. Based on this, the team is building a highly sensitive pathogen monitoring network and intelligent early warning system to improve the efficiency of epidemic response and the scientificity of public health decision-making. In the field of clinical diagnosis and new drug development, the center integrates AI with multi omics technology applications to analyze the immune metabolism profile of difficult infected patients and promote personalized diagnosis and treatment. Meanwhile, the center is utilizing AI to accelerate the development of antiviral drugs and vaccines.
Monkeypox virus and smallpox virus belong to the Orthopoxvirus genus and pose a serious threat to global health. Since smallpox vaccination stopped, the incidence rate of monkeypox has gradually increased, and there is an urgent need for prevention and control. In April of this year, the team, in collaboration with the Guangzhou National Laboratory Shanghai Base team, released a breakthrough in the research and development of a new Chinese anti monkeypox drug, which has broken through the bottleneck of existing international drugs. It has stronger efficacy and a wider antiviral spectrum, providing key technical reserves for dealing with future smallpox and other positive smallpox viruses. At present, the drug is about to enter the clinical approval stage. This achievement also marks a new model for accelerating the research and development of pandemic drugs for emerging infectious diseases through full chain cooperation.
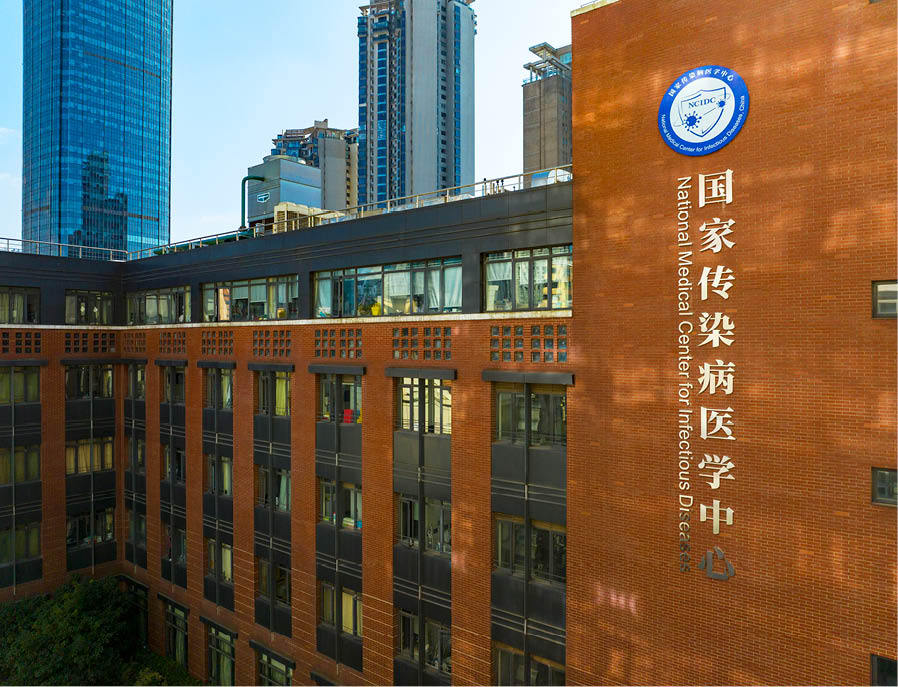

In the field of medical prevention integration, the National Center for Infectious Diseases is accelerating the analysis of multidimensional data such as epidemiology, environment, and genomics to promote ultra early warning of new infectious diseases and provide key support for pathogen identification, vaccine and new drug development
In more cutting-edge fields, as an important contributor to the "Chinese Brain Project", the Huashan Hospital team has achieved remarkable results in the field of brain computer interfaces, jointly with research institutes and innovative enterprises. This largely relies on the ability of AI algorithms to collect and analyze astronomical level information. By establishing direct interaction channels between the brain and external devices, brain computer interface technology is expected to become a key technology for reshaping patients' neurological function, helping patients with paralysis, aphasia, and other conditions rebuild their motor control, language communication, and perceptual feedback abilities.
Based on multiple successful clinical trials such as mind synthesis movement and mind synthesis language, led by Mao Ying from Huashan Hospital, the world's first multicenter clinical cohort study will be launched in May 2025 to systematically verify the long-term safety and universality of brain computer interface technology. Around the cutting-edge new technology of brain computer interface, Shanghai is about to establish a specialized branch for brain computer interface and neural regulation, gathering forces from the innovation chain of "industry university research medicine" in basic, clinical, and industrial fields, and achieving further breakthroughs in this Chinese original technology.
The innovative drug development and exploration of new technologies aided by AI are driving healthcare into a new era. In various scenarios of Huashan Hospital, it is clear that the 'future has arrived'.
AI integration makes healthcare warmer
Hospital management and medical process management are the most complex management areas in modern society. Huashan Hospital focuses on patient health management and uses AI and big data technology to build a smart service system that covers pre diagnosis risk warning, precise guidance during diagnosis, and full process tracking after diagnosis.
The Dermatology Department of Huashan Hospital receives an average of over 5000 patients per day and has an annual outpatient volume of over 1.9 million. It is the largest dermatology medical center in China and also the location of the National Skin and Sexually Transmitted Disease Professional Quality Control Center (planned).
In order to reduce patient waiting time and improve diagnosis and treatment efficiency, patients can now make precise appointments through the Huashan Hospital AI intelligent pre consultation system before entering the hospital. By guiding the formation of structured digital medical records in advance, doctors can already understand the core condition before seeing the doctor for face-to-face consultation, greatly reducing on-site writing time and allowing patients to feel respected for being understood in advance. At the same time, the hospital's dynamic number source allocation mechanism can intelligently adjust the time slot number source by analyzing the doctor's reception situation and patient appointment tendency in real time, alleviating the contradiction between "difficult to find number one" and "vacancy waste".
In the process of diagnosis, the hospital's intelligent system supports patients to complete medical procedures such as registration, check-in, waiting inquiry, instant payment, examination appointment, report inquiry, etc. with one mobile phone, reducing queuing time. The transparency of the process also reduces patients' waiting anxiety. After diagnosis, the Internet hospital provides extended services to facilitate the re diagnosis and prescription renewal of patients with chronic and common diseases. Patients can operate at home for five minutes, and drugs can be delivered to their homes. The monthly service volume exceeds 14000 person times, effectively solving the pain of repeated travel of long-term drug users.
The whole course management platform built by Huashan Hospital, based on disease types, integrates patient visits, medication, and treatment records into continuous health records. It actively pushes personalized health education, medication reminders, follow-up plans, and supports patients to self evaluate scales and query health indicators (such as weight and blood glucose) trends, becoming the digital center for patients' "active health".
While promoting the application of new technologies, Huashan Hospital fully considers elderly patients who are currently not proficient in using smart devices. On the second floor of the outpatient department of Huashan Hospital, there are public welfare courses every day. Volunteers teach patients step by step to familiarize themselves with the hospital's medical process and help elderly patients seek medical treatment conveniently.
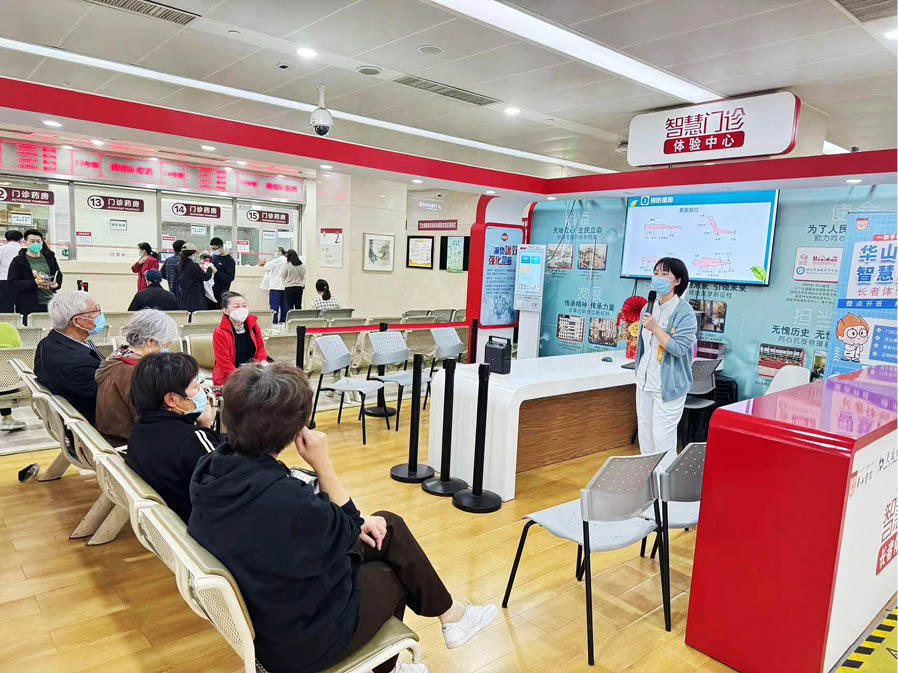

While promoting the application of new technologies, Huashan Hospital considers elderly patients who are currently unable to proficiently use smart devices and has opened a smart outpatient elderly center to teach them how to seek medical treatment on their mobile devices
With the integration of new technologies into the entire healthcare process, "AI governance" has become a new topic. Referring to the framework of the White Paper on Artificial Intelligence Governance, Huashan Hospital has established a governance system that covers "data security, ethical review, clinical verification, and application supervision" to ensure the security and compliance of technology applications. In the development of AI medical devices, technical reliability is ensured through multi center clinical validation, ethics committee review, and full process quality control.
AI, Nowadays, it has been integrated into various aspects of healthcare, and the transformation brought about by AI empowerment expands the boundaries of medicine with the power of technology, and warms the experience of life with the intelligence of data. Huashan Hospital is continuously exploring a series of practices to solve the problem of how to make good use of AI and make healthcare warmer in this era.
Huashan Hospital is facing the forefront of world technology and people's health needs, integrating hospital resources to create a new layout. In the wave of global AI integration into healthcare, it has embarked on a "Huashan Road" that leads innovation.




